Your Guide To Air Sampling, Testing and Monitoring

Achieving a clean, contamination-free environment requires testing for and monitoring of microbial presence on surfaces, people, and also air. Air is one of the critical contributors to microbial contamination in any environment. Bacteria, fungal cells and spores present in the atmosphere and have the ability to remain suspended for extended periods of time. This presence poses health and safety risks to not only people working in that environment, but also to the products being manufactured.
What is microbial air sampling and why is it important?
Microbial air sampling is one of the key components of environmental monitoring. As the name suggests, samples of air are collected and analyzed to detect the presence of microbial contamination.
The pharmaceutical and food and beverage industries are few of the many industries that regularly use qualitative and quantitative air sampling methods to validate environments for microbial contamination.
When comprehensive microbial air sampling is done in a timely and proactive manner, it helps in detecting contamination (and preventing cross-contamination) which otherwise can have serious consequences to personnel, environment and products.
Active air sampling vs passive air sampling
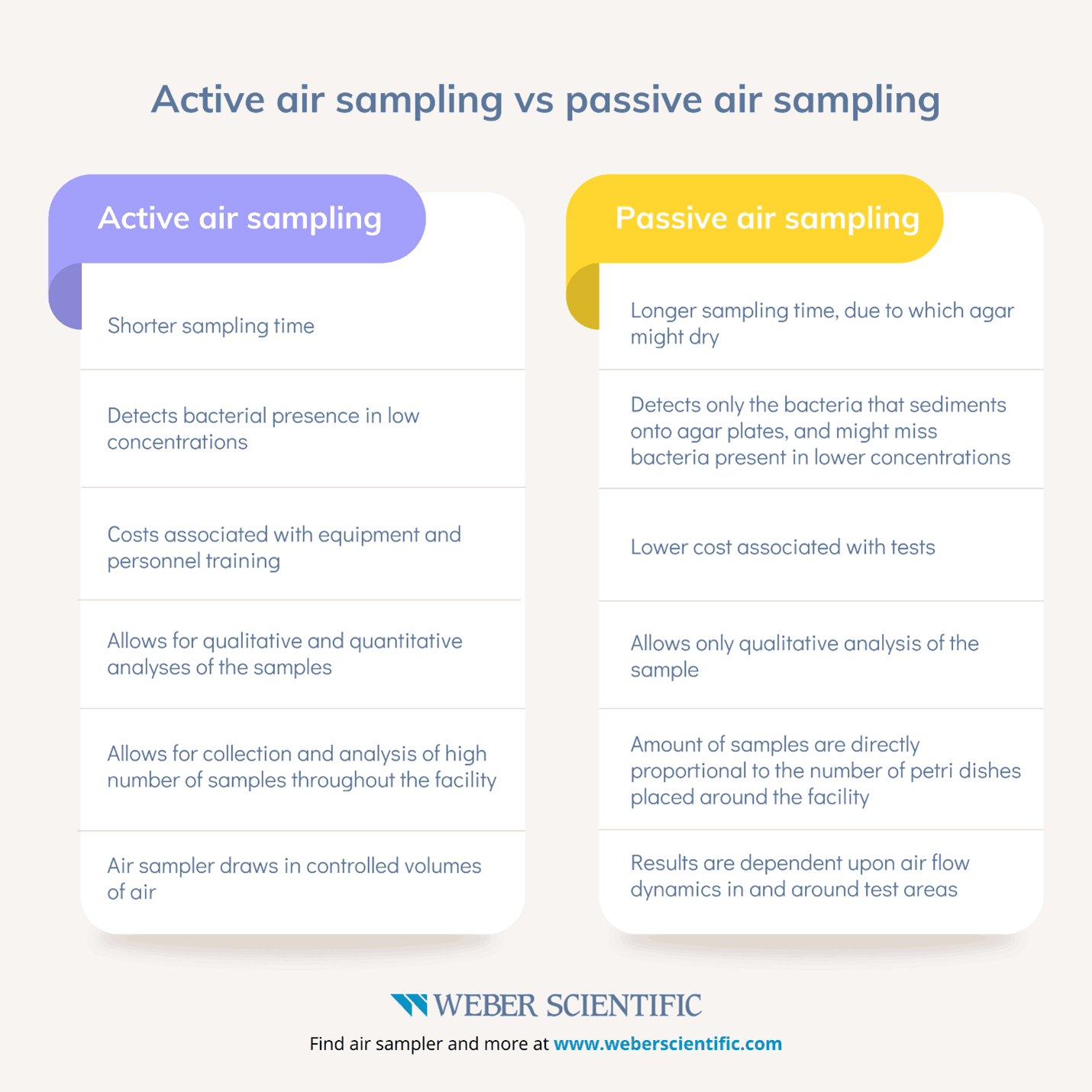
Passive air sampling
One of the methods for microbial air sampling is the use of a standard agar plate that is placed, open to the air, in a test area. Known as passive air sampling, such a method detects microbial contamination that drops from the air (sediments) onto the agar plate, and grows on the culture media.
These plates are later incubated to create optimal growth conditions for target bacteria. Any growth of the bacteria is later enumerated to determine the amount of microbial contamination in that environment. Since the agar plate is simply placed in a test area, its results are heavily determined by air flow dynamics in the room.
Easygel®’s Total Count media and T-Salt Nutrient media are effective to detect indoor air contamination.

Active air sampling
Complementing passive air sampling is active air sampling, which allows for both qualitative and quantitative analyses of the collected sample.
Active air sampling uses equipment, usually a microbial air sampler, to draw measured volumes of air through the device. In most cases, the device will use a petri dish with culture media in it. When the air reaches the petri dish, any microbes in the air embed themselves onto the culture media.

Similar to passive air sampling, the petri dishes are then incubated to allow any microorganisms to form colonies.
Active air sampling allows for determination of the number of viable microorganisms per cubic meter of air, offering both qualitative and quantitative analyses.
What's the difference between air sampling and air monitoring?
Air sampling is akin to taking a quick picture of the environment at that particular point in time whereas air monitoring is documenting the changes in air quality and contamination over time.
Choosing between passive and active air sampling really depends on the testing requirements and goals. In most cases, both methods complement each other in terms of qualitative and quantitative analyses, costs, and time needed for testing.
Get in touch with Weber Scientific for a consultation about the appropriate sampling and monitoring methods for your facility.

